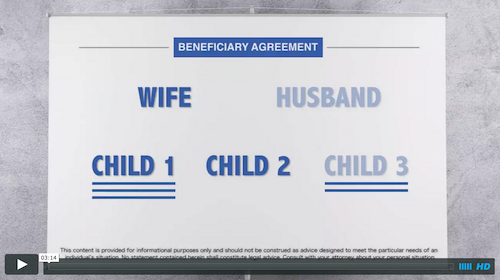
As you prepare your financial strategies, it’s important to spend some time considering beneficiary arrangements. Whether it’s through an IRA, life insurance, wills or trusts, anytime you want to leave money to others, you want make sure that you have in your mind a good understanding of how you want to designate the beneficiary.
For example, let’s say you’re a husband and a father and you have money in a retirement account — an IRA. Typically, your primary beneficiary will be your wife. What does that mean? It means that if you die and your wife is still alive, your wife will receive all the proceeds of that account. The wife in this scenario is considered a primary beneficiary. But what if your wife dies before you?
Or what if you and your wife die at the same time? In this scenario you may want what are called secondary or contingent beneficiaries. Let’s say you and your wife have three children: child one, two and three. These children can be named as a second line of beneficiaries, or contingent beneficiaries, so just in case your wife dies before you do, or you and your wife die at the same time, you’ve got the second line of beneficiaries, the three children. You may choose to divide the proceeds of your retirement account evenly between the three children — a third/a third/and a third.
But here’s something else to consider. What if your children have children of their own, your grandchildren? Let’s say child No. 1 has 3 children child No. 2 has no children at all and child No. 3 has two children — meaning you have a total of five grandchildren. Now, you may want to start asking some additional questions about designating beneficiaries.
Let’s assume your wife dies before you. Now there is only you. Therefore, when you die, the proceeds are designated to go to your three children who you have named as contingent beneficiaries. Well, what if one of your children dies before you? Let’s say your third child, the one with two children, dies before you .Then what happens? Well, if you haven’t set up your beneficiaries appropriately, you could end up disinheriting those two grandchildren. All of the proceeds could end up going to child one and child two, cutting out your third child’s surviving children.
That’s generally not what people want. Instead, they may say, “We want this child’s share to go to his/her two children.” This is generally referred to as a per stripes distribution, meaning that each branch of the family is to receive an equal share. If that is your objective, you would want to incorporate that term into your beneficiary designations. Then, should both your wife and one of your contingent beneficiaries die before you, the beneficiary designation would direct that contingent beneficiary’s share of the proceeds to go to his/her heirs.
This content is provided for informational purposes only and should not be construed as advice designed to meet the particular needs of an individual’s situation. No statement contained herein shall constitute legal advice. Consult with your attorney about your personal situation.


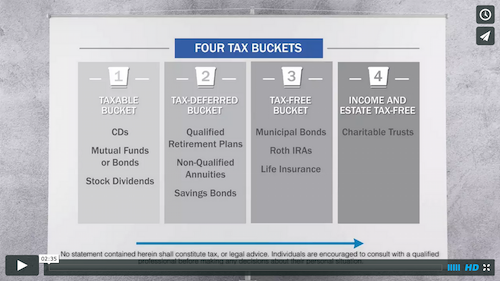







 One of the biggest retirement planning mistakes you can make is to underestimate the amount you’ll need to save by the time you retire. Focus on your actual expenses today and think about whether they’ll stay the same, increase, decrease, or even disappear by the time you retire. While some expenses may disappear, like a mortgage or costs for commuting to and from work, other expenses, such as health care and insurance, may increase as you age. If travel or hobby activities are going to be part of your retirement, be sure to factor in these costs as well.
One of the biggest retirement planning mistakes you can make is to underestimate the amount you’ll need to save by the time you retire. Focus on your actual expenses today and think about whether they’ll stay the same, increase, decrease, or even disappear by the time you retire. While some expenses may disappear, like a mortgage or costs for commuting to and from work, other expenses, such as health care and insurance, may increase as you age. If travel or hobby activities are going to be part of your retirement, be sure to factor in these costs as well. Source: jemstep.com
Source: jemstep.com

 Your marriage lasted 10 years or longer
Your marriage lasted 10 years or longer

